مقدمة
لقد زاد استخدام تقنية RFID كحل حديث لجمع البيانات بشكل مطرد عامًا بعد عام، ومن المتوقع أن يقترب سوق RFID العالمي من 32 مليار دولار أمريكي بحلول عام 2023. ويعود نمو RFID بشكل أساسي إلى تعدد استخداماته كحل، العائد المحتمل على الاستثمار في التطبيقات الممكنة، وسهولة الاستخدام النسبية بعد التثبيت.
يُستخدم نظام RFID بشكل أساسي لفتح الأبواب وتتبع الحيوانات. ومن وجهة نظر التكلفة والقدرة، أصبح الأمر أكثر جدوى من أي وقت مضى. ناهيك عن أن قيمة البيانات القابلة للتنفيذ وصلت إلى أعلى مستوى في التاريخ. إن سلسلة التوريد والرعاية الصحية والتصنيع والقنب ليست سوى بعض من الصناعات العديدة التي تستخدم تقنية RFID للعمل بكفاءة أكبر. حتى مع النمو الأخير لجميع الصناعات في مجال RFID والتكنولوجيا بشكل عام، لا يزال هناك مجال للنمو في تطبيقات RFID ذات درجة الحرارة العالية - وخاصة التطبيقات التي تتطلب التعرض لفترات طويلة لدرجات حرارة أعلى من 150+ درجة مئوية (302+ فهرنهايت).
إذن ما مشكلة ارتفاع درجة الحرارة؟ أليست علامات RFID ذات درجة الحرارة العالية متاحة بالفعل؟
هناك العديد من علامات درجات الحرارة المرتفعة المثيرة للإعجاب في السوق (قم بالتمرير لأسفل لرؤية خيارات علامات درجات الحرارة المرتفعة الشائعة)، ولكن هناك أيضًا قيودًا على التطبيقات الممكنة. من أجل فهم العوائق التي تسببها درجات الحرارة المرتفعة بشكل كامل، دعونا أولاً نفحص تكوين بطاقة RFID، وكيفية عملها، وكيفية تصنيعها.
مكونات علامات RFID
بالمقارنة مع علامات RFID النشطة، تُستخدم علامات RFID السلبية بشكل أكثر شيوعًا في تطبيقات درجات الحرارة المرتفعة لأنها أكثر فعالية من حيث التكلفة. يبدأ تطوير العلامات السلبية عادةً بثلاثة مكونات أساسية:
الهوائي - عادة ما يكون مصنوعًا من معدن موصل أو رقائق معدنية أو حبر معدني مطبوع، ويستقبل الهوائي ويرسل إشارات الراديو.
الدوائر المتكاملة - غالبًا ما تسمى بالرقائق أو الدوائر المتكاملة، الدوائر المتكاملة بحجم إبرة تقريبًا، مصنوعة من السيليكون، وهي "عقل" العلامات التي تخزن البيانات.
الركيزة: طبقة رقيقة من المادة، عادة ما تكون بلاستيكية، تعمل على ربط الشريحة والهوائي معًا.
في هذه المرحلة، يتم تطبيق طبقة أخرى من مادة تسمى "الوجه" لتغطية الهوائي المكشوف والرقاقة، وتشكيل "بطانة". يتم بيع البطانة إما إلى المستخدم النهائي أو تمريرها خلال مرحلة أخرى من التطوير لتصبح ملصقًا أو ملصقًا نهائيًا. في حالة معظم الملصقات ذات درجة الحرارة العالية، يتم تغليف البطانة بمادة لدنة حرارية أو سيراميك أو مواد أخرى مقاومة للحرارة لحماية مكونات عمل الملصق من درجات الحرارة المرتفعة والبيئات الصناعية القاسية.
كيف تعمل علامات RFID السلبية؟
باختصار، عندما يقوم قارئ RFID بتوليد موجات تردد راديوية منبعثة من خلال الهوائي، يقوم الهوائي الداخلي للعلامة ضمن نطاق القارئ بتوصيل طاقة موجة الراديو إلى شريحة العلامة. تعمل طاقة موجة الراديو على تنشيط الشريحة، وتقوم الشريحة بتعديل الطاقة باستخدام بيانات العلامة وتنقل الإشارة المعدلة مرة أخرى إلى القارئ و/أو الهوائي.
Problem lies in
The size is usually compared with a needle or a grain of sand. The RFID chip must be fixed on a very thin metal tag antenna so that the energy conducted by the antenna activates the chip and accesses the stored data. The chip is usually soldered to the antenna or connected with epoxy. This combination between the tag chip and the antenna is the most vulnerable part of the tag.
The vulnerability is due to the physical composition of the material used to connect the chip to the antenna. If exposed to high temperatures for a long time, even the strongest epoxy and solder metals will melt. If the adhesive becomes weak, the chip will separate from the antenna, rendering the tag useless.
High temperature takeaway
These two terms are the key to evaluating high-temperature labels:
Operating Temperature-The temperature range within which the RFID tag can work normally during its lifetime.
Maximum exposure temperature-the highest temperature that an RFID tag can withstand without affecting the structure and/or performance of the tag.
By maintaining the highest exposure temperature, the chip should remain in place and the label material will remain intact. Most high-temperature label manufacturers will also include important label exposure intervals based on extensive testing.
If a high-temperature label is exposed to high temperatures, it is important to ensure that the label will not be read until the temperature of the label itself is within the operating temperature range of the label. This is because the material connecting the chip to the antenna may not be solid and therefore cannot conduct radio frequency energy as expected. Attempts to read tags at high temperature levels may compromise the chip's data. After a high-temperature label is exposed to high temperatures, its packaging is designed to maintain the internal structure of the label and to dissipate heat, which helps the label to return to its working temperature.
Tag Specification Example:
1. High Temperature Resistance Anti Metal UHF Hard Tag
This tag is specially designed to resistant high temperature (under 230°С for 1hours without damage), chemicals, pressure and torsion. The tag operates with UHF chip and can survive in harsh environments,mainly used in industry equipment,manufacturing,automobile manufacturing,oil & gas & mining.
Reliability testing terms and results:
Withstand 230°С for 1 hours continuously without damage.
Passed the 95% alcohol test.
No. 92 gasoline wipe passed.
Material passed SGS certification
Passed Ultrasonic cleaning test
IP68

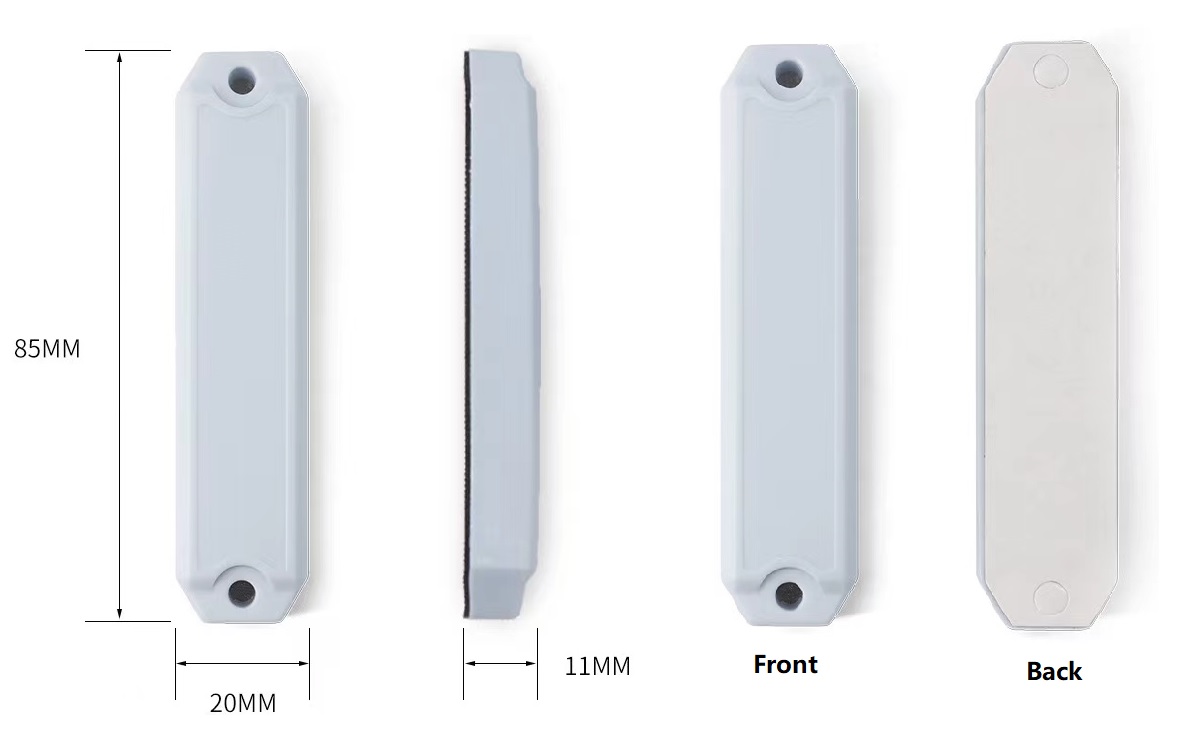
2. UHF ABS On Metal Tag For Pallet Management
This product can be widely used in indoor and outdoor asset management and inspection management. It can achieve good radio frequency performance when installed on metal and non-metal surfaces. The product performance is stable and reliable.Available chips can be Impinj M4QT,R6,etc.
Features:
Rugged tag,can be used in a harsh environment
شريحة Impinj M4QT أو أنواع شرائح UHF الأخرى
طريقتان للتركيب على الأصول: لاصقة أو مثبتة بالمسامير
حجم صغير: 80 مم × 25 مم × 11 مم
أداء عالي: مسافة قراءة تصل إلى 8 أمتار.
تطبيق مرن: إدارة الأصول، وإدارة المنصات، وإدارة المعدات.